Category:Heat Map: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(→�) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
https://www.andrewnoske.com/wiki/Code_-_heatmaps_and_color_gradients | https://www.andrewnoske.com/wiki/Code_-_heatmaps_and_color_gradients | ||
Track history can be visualised as heatmaps directly | === Heat maps in GDK === | ||
Track history can be visualised as heatmaps directly: | |||
http://docs.maria.teleplanglobe.com/Track_history#Track_history_heatmap | http://docs.maria.teleplanglobe.com/Track_history#Track_history_heatmap | ||
In addition, heat maps are implemented as a separate layer in Maria GDK. IHeatMapLayerViewModel exposes the heat map API: | |||
<source lang="c#"> | <source lang="c#"> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
=== Adding positions === | === Adding positions === | ||
=== Adding positions === | |||
Positions are addud using '''IHeatMapLayerViewModel.HeatMapGroups''' | |||
<source lang="c#"> | |||
public static HeatMapGroup CreateTestGroup(string fileName) | |||
{ | |||
PositionGroupCollection testData; | |||
using (var stream = File.Open(fileName, FileMode.Open)) | |||
testData = PositionGroupCollection.Parser.ParseFrom(stream); | |||
var result = new HeatMapGroup | |||
{ | |||
Settings = new HeatMapGroupSettings {KernelShape = KernelShapeEnum.Triweight}, | |||
Name = !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(testData.Name) ? testData.Name : NameFromFileName(fileName) | |||
}; | |||
foreach (var item in testData.PositionGroups) | |||
{ | |||
var hdi = new HeatMapItemData | |||
{ | |||
Id = item.Name, | |||
GeoData = new HeatMapGeoData(item.Positions.Select(a => new GeoPos(a.Lat, a.Lon)).ToArray()) | |||
}; | |||
result.Add(hdi.Id, hdi); | |||
} | |||
return result; | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
=== Heat map settings === | === Heat map settings === | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 17 November 2020
General
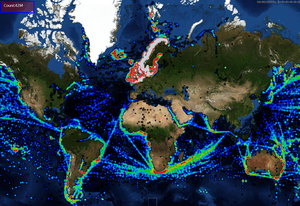
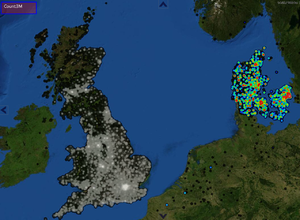
Heat maps are typically used to indicate density of data points geographically using color coding. They can be used to visualise large amounts of point data in 2D.
Examples include:
- Historical positions
- Population densities
- Frequency of events
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heat_map
Typically, bright of "hot" colors are used to indicate high level of activity or denser areas while "cooler" colors are used to indicate lower levels of activity. Several different palettes can be used for heatmaps. Some examples can be found here: https://www.andrewnoske.com/wiki/Code_-_heatmaps_and_color_gradients
Heat maps in GDK
Track history can be visualised as heatmaps directly: http://docs.maria.teleplanglobe.com/Track_history#Track_history_heatmap
In addition, heat maps are implemented as a separate layer in Maria GDK. IHeatMapLayerViewModel exposes the heat map API:
namespace TPG.GeoFramework.HeatMapLayer
{
/// <summary>
/// View model for general heat maps
/// </summary>
public interface IHeatMapLayerViewModel:IGeoLayerViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// Heat map data is organized in HeatMapGroups. Each group contains clusters of heat map data.
/// Separate settings and color palettes can be set for each group.
/// Note that the heat map property setters are applied to both default settings and to all groups.
/// For detailed, individual group settings control, access elements in the HeatMapGroups directly
/// </summary>
ObservableCollection<HeatMapGroup> HeatMapGroups { get; }
/// <summary>
/// HeatMapSettings contain global settings and a default group setting that
/// is used when no settings are available for a heat map group.
/// </summary>
HeatMapSettings HeatMapSettings { get; }
/// <summary>
/// Sets kernel radius unit (meters or pixels)
/// </summary>
KernelRadiusUnitEnum KernelRadiusUnit { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Kernel radius, unit controlled by KernelRadiusUnit
/// </summary>
UInt32 KernelRadius { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Sets kernel shape. The kernel shape controls how values are smoothed in the HeatMap.
/// See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_(statistics)#Kernel_functions_in_common_use
/// </summary>
KernelShapeEnum KernelShape { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Max pixel radius used when applying kernel. This is relevant when setting the kernel unit to "meters"
/// and is used to limit demanding calculations
/// </summary>
double MaxPixelRadius { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Multiplier is applied to all values prior to applying the kernel
/// </summary>
double ValueScale { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Smaller grid cell sizes yield higher quality heat maps. Larger grid cell sizes are quicker. Typical range is 1-10.
/// </summary>
int GridCellSize { get; set; }
}
}
Adding positions
Adding positions
Positions are addud using IHeatMapLayerViewModel.HeatMapGroups
public static HeatMapGroup CreateTestGroup(string fileName)
{
PositionGroupCollection testData;
using (var stream = File.Open(fileName, FileMode.Open))
testData = PositionGroupCollection.Parser.ParseFrom(stream);
var result = new HeatMapGroup
{
Settings = new HeatMapGroupSettings {KernelShape = KernelShapeEnum.Triweight},
Name = !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(testData.Name) ? testData.Name : NameFromFileName(fileName)
};
foreach (var item in testData.PositionGroups)
{
var hdi = new HeatMapItemData
{
Id = item.Name,
GeoData = new HeatMapGeoData(item.Positions.Select(a => new GeoPos(a.Lat, a.Lon)).ToArray())
};
result.Add(hdi.Id, hdi);
}
return result;
}
Heat map settings
Heat map colors
Standard colors
Custom colors
Multiple heat map groups
This category currently contains no pages or media.