Comparing 32 bit and 16 bit elevation GeoPackages
The tiled gridded coverage GeoPackage extension allows 32-bit source data to be converted to a GeoPackage with 16-bit integer tiles in PNG format, and still retain a significant number of decimals. This is accomplished by calculating a scale and offset for each tile, and store these in a separate table. This allows every tile to utilize the full range of the UInt16 data type (0-65536). Each tile is converted from Float32 to UInt16 as follows:
offset = min(tile)
scale = (max(tile) - min(tile)) / (2^16 - 2)
tile_png = (tile - offset) / scale
This formula entails that the less variation within a tile, the more of the original 32 bit precision can be retained. Leaning on Tobler's law of geography, we can assume that the variations in the terrain within any single tile will, on average, be quite small.
Method
This article tests the difference between a 32 bit and 16 bit geopackage, converted from a high-resolution DTM covering a large and hilly region of Norway. The source dataset have the following properties:
| Name | Data type | Format | Compression | Resolution | Projection | File count | Vertical accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasjonal Detaljert Høydemodell area 11-11 | Float32 | GeoTIFF | LZW | 1 meter | UTM 33 | 100 | At best 10 cm |
To compare the two GeoPackages we do simple raster arithmetic - subtract the 16-bit dataset from the 32-bit dataset, and examine the statistics of the resulting raster dataset as a whole.
Note on converting from Float32 source data to 16-bit GeoPackage
When GDAL opens a GeoPackage with 16 bit PNG tiles, it will examine the field precision in the gpkg_2d_gridded_coverage_ancillary table. If this value is 1.0 (which is default), pixel values will be rounded to the nearest integer after scale and offset is applied. This also applies that any program which relies on GDAL to open the GeoPackage (i.e. FME, QGIS etc.). Maria GDK, on the other hand, will always return data type double after scale and offset is applied, regardless of the value of precision.
Also note that if gdaladdo is used to build overviews on a 16bit GeoPackage with precision=1.0, the basis for the calculations will be integers, and so the overviews will in turn be permanently created with integer values. This leads to a distinct stair-case effect, and will be present in all software.
To ensure that float values are returned in all software, precision must be set to anything other than 1.0. This is done by simply specifying creation option -co precision=0.0001 when creating the GeoPackage. For example, a full command to convert from 32 bit to 16 bit data could look like this:
gdal_translate -of GPKG -co tile_format=PNG -co precision=0.0001 input32bit.tif output16bit.gpkg
Result
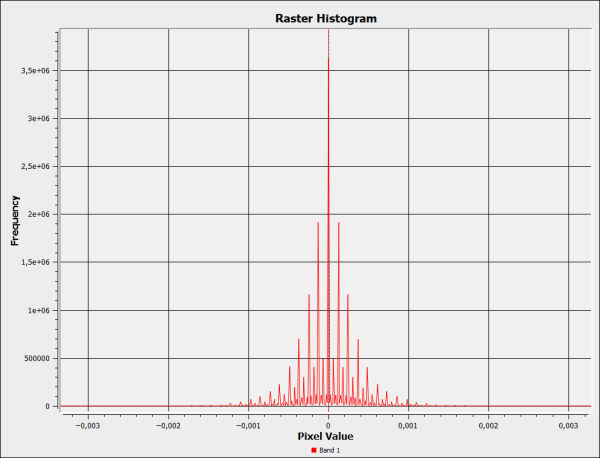
The resulting raster values are evenly distributed on both sides of zero. When we calculate the statistics, we use the absolute values from the restult.
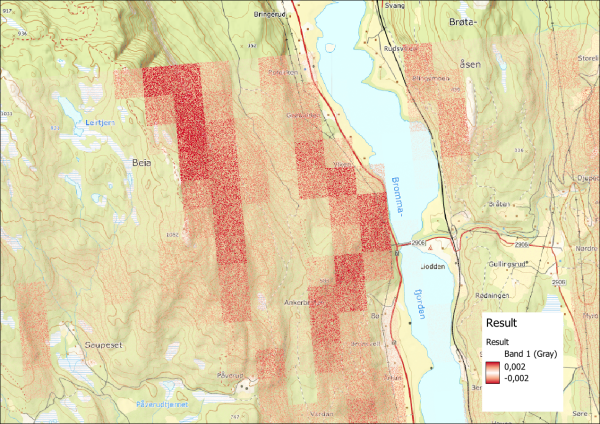
The result shows that the difference between the 32 bit and 16 bit GeoPackages is very small. The average of 0.2 millimeters is several orders of magnitude smaller than the assumed vertical accuracy of the dataset. When visualized in a map, the result shows that the discrepancy between the datasets is largest in steep terrain, as expected.
| Max | Mean | Std.dev. |
|---|---|---|
| 0.18328857 | 0.00023618 | 0.00025333 |