Getting started with Maria Map Maker
Maria Map Maker (M3) is an application to create, edit and manage maps. These maps can be used in other applications built with the MARIA Geo Development Kit (GDK).
This guide will take you the shortest path from first-time startup to a finished map. You will also hopefully get a feel for the workflow in M3.
Concepts
We begin with a quick explanation of a few key concepts in M3. These terms will probably sound familiar, but we will explain what they mean in M3.
Workspace
A workspace is simply a folder containing one or more products. The workspace should only contain products created by M3 - no subfolders or loose files. Working with maps requires a lot of reading and writing from disk. This means that you should create your workspace on a fast storage device (such as a local SSD) if possible.
Product
The product is the basic container for map data and all related files. It also contains metadata describing the product and its contents. The product ususally contains one or more datasets with the same theme, covering a specific geographical area.
The product consists of a folder on disk, with a specific naming scheme: <Product name>_<Sequence number>_<Version ID>
Example: NorwayTopoRaster_v25_db95990c
Basemap/overlay
The basemap and the overlay are lists of map layers, where each layer is a reference to an existing raster or vector dataset, or the address of a web map. Information about visibility, scales and draw order is also stored here.
Basemaps and overlays are the starting points for editing maps in M3. They are also the entry point to your maps when they are used in other MARIA GDK applications.
Example: Norway Topo Raster N50 - N5000
Dataset
The dataset is the actual geographical data, with accompanying styling information and metadata. Datasets are always stored in a product. A dataset comes in a variety of types in M3:
- Vector
- Raster
- Elevation
- 3D
- Location
- Routing
Step by step instructions
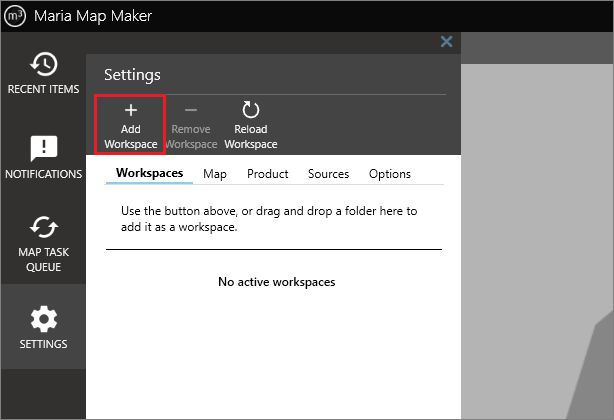
1. Set up workspace
When starting up Maria Map Maker for the first time, it's necessary to define a workspace. This could be a folder where you have some existing products, or an empty folder where you intend to create new products. Click the SETTINGS button on the left sidebar, and the Workspaces tab will be the first option. Each workspace you add gets its own button on the sidebar.
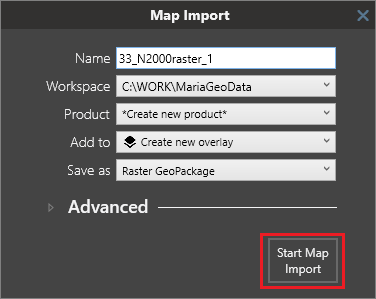
2. Import data
Now that you have a workspace configured, you can start importing data. In this example, we have a simple GeoTIFF file. The quickest way to import it is to simply drag and drop it on the map area. This will open the Map Import dialog. We will leave all the options as they are. This will automatically create a new product and a new overlay for the dataset we're importing.
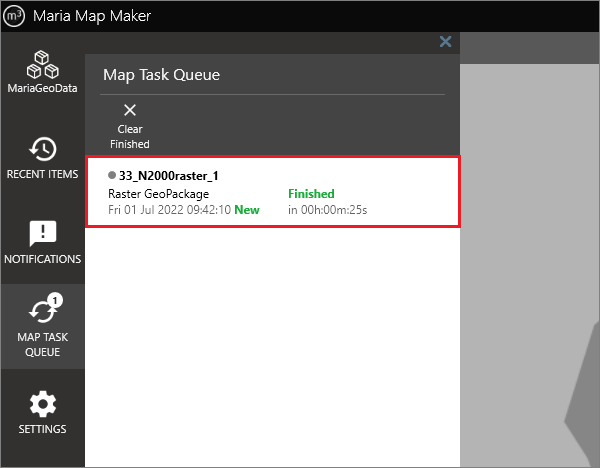
3. Map task
Starting the import creates a Map Task, which you can follow in the Map Task Queue window. When the Map Task is finished, you can double-click it to open the new product it was imported to.
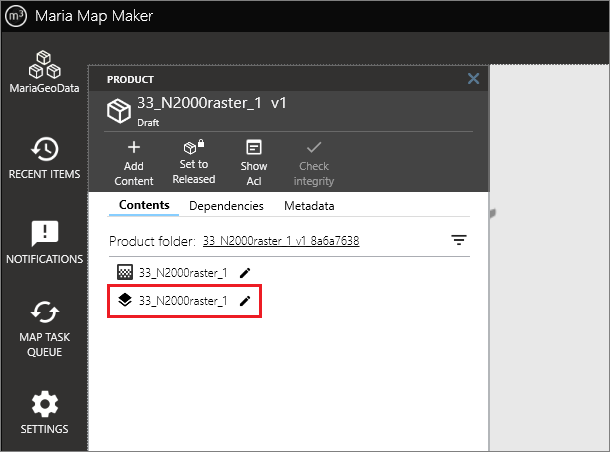
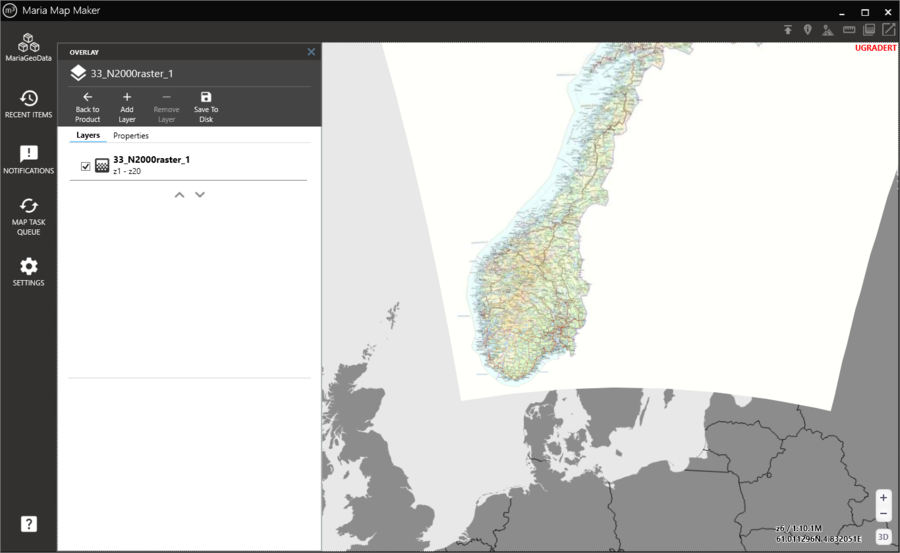
4. Open overlay
You now see the contents of the product - a raster dataset and an overlay. All editing and viewing of map datasets is done via the overlay, so double-click it to see your dataset in the map.
5. Finished
You are now looking at the overlay. It contains a single layer - a reference to the raster dataset you just imported. The dataset should be visible in the map area. Your product is now ready to be used in any application based on MARIA GDK.