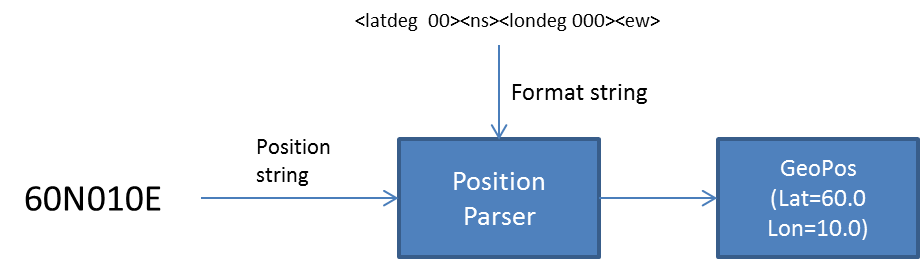
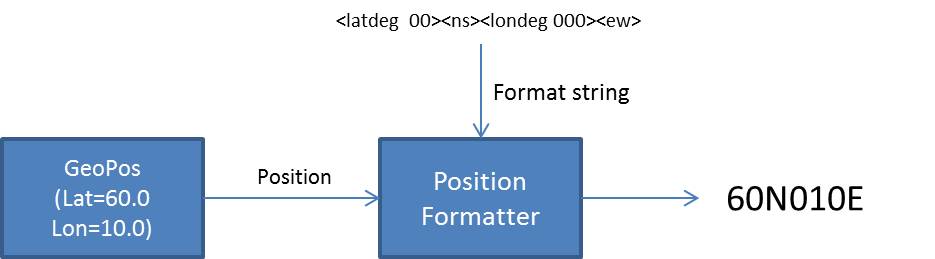
Position parsing and formatting
Maria GDK includes a utility for parsing and formatting geographical positions. Focus is on flexibility and generality over raw performance.
Overview
This document is intended for Maria GDK developers and system integrators.
LinqPad (www.linqpad.net) was used to run the examples in this document. Alternatively, a standard Visual Studio C# project can be used to run the sample code. TPG.GeoUnits.dll contains the required definitions. Make sure also to add namespaces (TPG.GeoUnits and TPG.GeoUnits.Contracts). Press F4 to add assembly reference in LINQpad.
Position formats can vary significantly depending on user preferences and input sources. The same position can be represented in multiple ways. For instance, the position 60N10E can be written as:
60°00'00.0"N010°00'00.0"E (DMS) 60 00.0000N 10 00.0000E (DM) 32V NM 55776 51833 (MGRS) NLLA 0000 00 00 00 (Georef)
Using methods exposed by IGenericPositionFormatter and IGenericPositionParser, these types of position representations can easily be generated and parsed:
IGenericPositionFormatter formatter=new GenericPositionFormatter();
IGenericPositionParser parser=new GenericPositionParser();
GeoPos pos=new GeoPos(60.0, 10.0);
string dmpos=formatter.FormatPosition(pos, "<latdeg 00><latmin 00.0><ns><londeg 000><lonmin 00.0><ew>", null);
string mgrspos=formatter.FormatPosition(pos, "<mgrs>", null);
string dmsformat="<latdeg 00>°<latmin 00>'<latsec 00.0>\"<ns><londeg 000>°<lonmin 00>'<lonsec 00.0>\"<ew>";
string dmspos=formatter.FormatPosition(pos, dmsformat, null);
dmpos: 6000.0N01000.0E\ mgrspos: 32V NM 56 52\ dmspos: 60°00'00.0"N010°00'00.0"E
Parsing uses the same formatting string as FormatPosition:
GeoPos ?p=parser.Parse(dmpos, "<latdeg 00><latmin 00.0><ns><londeg 000><lonmin 00.0><ew>", null);
| 60 00 00.00N 10 00 00.00E | ||
| Lat | 60 | |
| Lon | 10 | |
| IsValid | True | |
Implementation
GenericPositionFormatter
IGenericPositionFormatter and implementation GenericPositionFormatter are used to format position strings. See code-documentation for details.
Format method is used to transform numeric GeoPos to string representation. Note the CultureInfo parameter, it is used to set decimal sign:
IGenericPositionFormatter gpf = new GenericPositionFormatter();
GeoPos pos=new GeoPos(60.0, 10.0);
gpf.Format(pos, "<latdeg *.0><ns><londeg *.0><ew>",
CultureInfo.InvariantCulture).Dump();
gpf.Format(pos, "<latdeg *.0><ns><londeg *.0><ew>",
new CultureInfo("NO")).Dump();
//60.0N10.0E\ 60,0N10,0E//
GenericPositionParser
IGenercPositionParser and implementation GenercPositionParser are used to parse position strings.
Parse method is used to parse position string to GeoPos object. If parsing fails, return is null.
IGenericPositionParser parser=new GenericPositionParser();
GeoPos ?pos=parser.Parse("60N10E","<latdeg ##><ns><londeg ###><ew>", null);
pos.Value.Dump();
| 60 00 00.00N 10 00 00.00E | ||
| Lat | 60 | |
| Lon | 10 | |
| IsValid | True | |
FormatStringToRegex retrieves regular expression for format string and can be used to validate position strings or extract position strings from text documents without actually parsing. Another use is for debugging format strings:
IGenericPositionParser parser=new GenericPositionParser();
string regexString=parser.FormatStringToRegex(
"<latdeg ##><ns><londeg ###><ew>", null);
bool matchOk=Regex.IsMatch("60N20E",regexString);
bool matchErr=Regex.IsMatch("600N20E",regexString);
regexString.Dump();
matchOk.Dump();
matchErr.Dump();
%%^%%\s%%*(%%?'latdeg'\d?\d?)(?'ns%%'[%%nNsS])(?'londeg'\d?\d?\d?)(?'ew%%'[%%eEøØwWvV])\s*$\ True\ False
Predefined format strings
TPG.GeoUnits.PositionFormatDefinitions contains definitions for existing position formats. Note that the formatting used in the generic formatting/parser classes allows parsing and formatting of all entries in PositionFormats.
The predefined format strings provide verified examples and can be used as a base for creating custom format strings.
Format string syntax
The format strings can contain three types of data: Elements, whitespace and freetext. All elements are used both in formatting and parsing.
Elements
<latdeg>, <londeg>, <latmin>, <lonmin>, <latsec>,<lonsec>
Represent components of latitude (<lat%%***%%>) and longitude (<lon%%***%%>). Each of these elements also requires number formatting, for instance
<latdeg ##>-<londeg ###>
# is used for optional digit. When formatting, only the required number of digits are used. 0 is used for mandatory digit. Zero-padding is used when formatting. . - decimal sign. Optional when parsing. Depends on culture info * -- Zero or more digits
It is possible to specify separate number formats for parsing and formatting:
var parser = new GenericPositionParser();
var formatter = new GenericPositionFormatter();
string formatString="<latdeg #0.# 00.0><ns><londeg ##0.# 00.0><ew>";
GeoPos ?pos=parser.Parse("60N10E",formatString, null);
string posString=formatter.Format(pos.Value, formatString, null);
posString.Dump();
outputs 60.0N10.0E
This allows full control of output digits and flexible parsing at the same time.
<ns>, <ew>, <øv>
North-south and east-west marker. Format or parse NS and EW marker. <øv> outputs "Ø" for east and "V" for west. Other national markers may be added in the future.
The markers can be placed at any location in the format string. To ensure correct parsing, only one ns-marker and one ew marker should be placed. When formatting, this restriction does not apply.
By default, the marker will be displayed according to value of output text, not the actual position value. For instance,
string formatString1="<ns><latdeg *0.#><ew><londeg *0.#>";
string formatString2="<ns><latdeg *0.###><ew><londeg *0.###>";
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(-0.01,-0.01), formatString1, null).Dump();
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(-0.01,-0.01), formatString2, null).Dump();
N0E0 S0.01W0.01
Note that "N" or "S" depends on position precision.
To display "N" or "S" markers based on sign of numeric/real position, use <ns real>, <ew real>, <øv real>:
string formatString1="<ns real><latdeg *0.#><ew real><londeg *0.#>";
string formatString2="<ns real><latdeg *0.###><ew real><londeg *0.###>";
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(-0.01,-0.01), formatString1, null).Dump();
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(-0.01,-0.01), formatString2, null).Dump();
S0W0 S0.01W0.01
Sign marker
Lat-lon positions can be parsed and represented using sign instead of N/S, E/W markers. Insert a '-' before the numerical formatting string, example:
<latdeg -*0.####>°,<londeg -*0.####>°
This will allow parsing and formatting of positions on the format "-31.1390°,-079.6582°". Note that omitting the sign marker will display unsigned values in order to maintain consistency.
<mgrs>
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Military_grid_reference_system
MGRS - military grid reference system. Optional number 1-5 specifies number of coordinate digits.
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(60,10), "<mgrs 1>", null).Dump();
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(60,10), "<mgrs 5>", null).Dump();
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(60,10), "<mgrs>", null).Dump();
32V NM 6 5 32V NM 55776 51833 32V NM 56 52
<georef>
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Georef
Georef -- World Geographic Reference System.
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(60,30,40,10,30,40), "<georef>", null).Dump();
NLLA 3030 66 66 66
<utm>
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Transverse_Mercator_coordinate_system
UTM - Universal Transverse Mercator
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(60,30,40,10,30,40), "<utm>", null).Dump();
32V 0582978 6709287
<utmlc2is>
This is a custom version used for NATO.
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(62.241, 10.4223), "<utmlc2is>", null).Dump();
N 32 0573903 6901840
<ups>
UPS - Universal polar stereographic coordinate system
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_polar_stereographic_coordinate_system
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(87.43000, 40.15449), "<ups>", null).Dump();
N 2184026 1781884
<mups>
MGRS in the polar regions
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Military_Grid_Reference_System#Polar_regions
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(87.43000, 40.15449), "<mups>", null).Dump();
ZBE8402581883
<gars>
GARS - Global Area Reference System
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Area_Reference_System
new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(new GeoPos(62.241, 10.4223), "<gars>", null).Dump();
381NS43
Freetext
Freetext can be inserted between elements, and are used both for parsing and formatting. When parsing, the freetext characters must be included in the position string.
string formatString="<ns><latdeg #0.# 00.0>Degrees<ew><londeg ##0.# 00.0>Degrees";
string posString=new GenericPositionFormatter().Format(
new GeoPos(60,30,40,10,30,40), formatString, null);
GeoPos pos=new GenericPositionParser().Parse(posString, formatString, null).Value;
posString.Dump();
pos.Dump();
N60.5DegreesE10.5Degrees
| 60 30 00.00N 10 30 00.00E | ||
| Lat | 60,5 | |
| Lon | 10,5 | |
| IsValid | True | |
Space
When formatting, spaces are treated as freetext. When parsing, any space placed outside of an element can be replaced by one or more spaces.